- Details
- Written by: po3dno
- Category: Windows
- Hits: 297
Resets the machine account password for the computer.
Syntax
Reset-ComputerMachinePassword
[-Server <String>]
[-Credential <PSCredential>]
[-WhatIf]
[-Confirm]
[<CommonParameters>]Description
The Reset-ComputerMachinePassword cmdlet changes the computer account password that the computers use to authenticate to the domain controllers in the domain. You can use it to reset the password of the local computer.
Examples
Example 1: Reset the password for the local computer
Reset-ComputerMachinePasswordThis command resets the computer password for the local computer. The command runs with the credentials of the current user.
Example 2: Reset the password for the local computer by using a specified domain controller
Reset-ComputerMachinePassword -Server "DC01" -Credential Domain01\Admin01This command resets the computer password of the local computer by using the DC01 domain controller. It uses the Credential parameter to specify a user account that has permission to reset a computer password in the domain.
Example 3: Reset the password on a remote computer
$cred = Get-Credential
Invoke-Command -ComputerName "Server01" -ScriptBlock {Reset-ComputerMachinePassword -Credential $using:cred}This command uses the Invoke-Command cmdlet to run a Reset-ComputerMachinePassword command on the Server01 remote computer.
For more information about remote commands in Windows PowerShell, see about_Remote and Invoke-Command.
Parameters
-Confirm
Prompts you for confirmation before running the cmdlet.
| Type: | SwitchParameter |
| Aliases: | cf |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | False |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-Credential
Specifies a user account that has permission to perform this action. The default is the current user.
Type a user name, such as User01 or Domain01\User01, or enter a PSCredential object, such as one generated by the Get-Credential cmdlet. If you type a user name, this cmdlet prompts you for a password.
This parameter was introduced in Windows PowerShell 3.0.
| Type: | PSCredential |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-Server
Specifies the name of a domain controller to use when this cmdlet sets the computer account password.
This parameter is optional. If you omit this parameter, a domain controller is chosen to service the command.
| Type: | String |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-WhatIf
Shows what would happen if the cmdlet runs. The cmdlet is not run.
| Type: | SwitchParameter |
| Aliases: | wi |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | False |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
- Details
- Written by: po3dno
- Category: Windows
- Hits: 259
В таких случаях, системный администратор обычно просто заново включал вылетевший компьютер в домен. Но для этого компьютер нужно перезагружать. Мне захотелось найти альтернативу такому решению, и как оказалось, оно существует. Для этого можно воспользоваться Powershell.
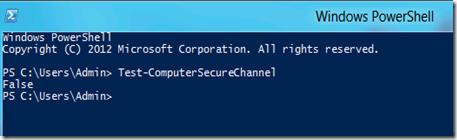
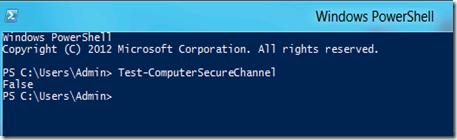
- Откройте консоль PowerShell
- Введите команду
Test-ComputerSecureChannel
- Если в ответ мы получим False, это означает что невозможно установить безопасный канал между клиентом и контроллером домена. А т.к. не устанавливается безопасный канал, то и залогинится с доменной учетной записью нельзя.
- Чтобы сбросить и синхронизировать пароль компьютера в домене, воспользуемся командой
Test-ComputerSecureChannel –Credential -Repair
- В появившемся окне введите имя пользователя, которому разрешено управлять учетной записью компьютера в домене и его пароль
- После чего еще раз проверим возможность установки безопасного канала первой командой, если все получилось, она вернет True
- Осталось выйти из системы и зайти под доменной учетной записью
- Details
- Written by: po3dno
- Category: Windows
- Hits: 222
After applying updates to a Windows image, cleanup the image and then export it to a new file:
md c:\mount\Windows
md C:\mount\temp
Dism /Mount-Image /ImageFile:"C:\Images\install.wim" /Index:1 /MountDir:C:\mount\Windows
Dism /Cleanup-Image /Image=C:\mount\Windows /StartComponentCleanup /ResetBase /ScratchDir:C:\mount\temp
Dism /Unmount-Image /MountDir:C:\mount\Windows /Commit
Dism /Export-Image /SourceImageFile:C:\Images\install.wim /SourceIndex:1 /DestinationImageFile:C:\Images\install_cleaned.wim- Details
- Written by: po3dno
- Category: Windows
- Hits: 285
+ Build new Server 2019 machine
# could be 2016 or even 2012R2
- vCPU = 4, vSocket = 1, RAM = 12 GB, PageFile = 32768 MB
- HDD1 = 150 GB, used for C drive (System)
- HDD2 = 3500 GB, used for D drive (WSUS data & content store, SQL Backup)
- HDD3 = 50 GB, used for G drive (SQL Data)
- HDD4 = 40 GB, used for H drive (SQL Temp DB)
- HDD5 = 40 GB, used for L drive (SQL Log)
+ Install SQL Server 2019 Standard
+ Update Windows & SQL server with Microsoft Online Updates
+ Add WSUS role
+ Configure WSUS role
- Update Files and Languages: Update Files tab, tick Download express installation files. Click OK
- Automatic Approvals: Tick the Default Automatic Approval Rule. Change the rule so that ONLY “Approve the update for all computers” is shown. Click the Advanced tab. Ensure all check boxes are ticked. Click OK
- E-Mail Notifications: Tick Send status report, set to Weekly, set time to 7.30am, set Recipient
- Set the outgoing SMTP server
- Personalization: Click round selector “Show Computer and status from this server alone”
+ Install WSUS reporting
- Find CLR type for SQL Server 2012 MSI and install. Its a challenge as the file is no longer on the Microsoft catalog site.
- Find Report Viewer MSI and install.
+ Optimize WSUS Configuration
# The need is to modify web.config parameters. Within an elevated CMD shell;
- sc stop wsusservice
- cd "C:\Program Files\Update Services\WebServices\ClientWebService"
- takeown /f web.config
- icacls web.config /grant administrator:(F)
- copy web.config web.config.org
- notepad web.config
# Find line;
<add key="maxInstalledPrerequisites" value="400"/>
# change this line to
<add key="maxInstalledPrerequisites" value="800"/>
# Find remark “MAXREQUESTLENGTH”, and then move to the line starting with
<httpRuntime maxRequestLength="4096" />
# change this line to
<httpRuntime maxRequestLength="204800" executionTimeout="7200" />
# Save web.config and exit notepad
+ Optimize IIS Configuration
# Within an elevated CMD shell;
- # Run IIS Admin
- %windir%\system32\inetsrv\inetmgr.exe
- # Navigate to <servername> \ Application Pools \
- # Right click on “WsusPool” and select Advanced Settings.
- # Make the following changes in the respective sub-sections shown in front left column;
General
Queue Length = 25000
Rapid-Fail Protection
“Service Unavailable” Response = TcpLevel
Failure Interval (minutes) = 15
Maximum Failures = 5
Recycling
Private Memory Limit (KB) = 0
Request Limit = 0
Virtual Memory Limit (KB) = 0
+ Restart Computer
- After 5 minutes, initiate testing on the WUA machine. No errors should occur, although scanning may take many minutes, even over an hour of slow low bandwidth WAN links.
- Results may include either no updates available which most likely means the WSUS is still updating its self (which can take days), or available updates are shown and are available for WUA to download and install.